Cannabis And Pain
The Use of Cannabinoids in Treating Neuropathic Pain: A New Hope
Neuropathic pain, often resulting from nerve damage or dysfunction, is a challenging condition to manage with conventional treatments. This type of pain can be chronic, debilitating, and resistant to standard pain relief methods, making it a significant concern for those affected. Cannabinoids, particularly tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD), have emerged as promising options for alleviating nerve-related pain. This article explores how these compounds work, the methods of administration, and potential side effects.
How Cannabinoids Alleviate Neuropathic Pain
The human body contains an endocannabinoid system (ECS), which plays a vital role in regulating pain, among other physiological processes. The ECS consists of receptors, endocannabinoids, and enzymes that work together to maintain homeostasis. Cannabinoids like THC and CBD interact with the ECS, particularly by modulating the activity of CB1 and CB2 receptors.
THC, known for its psychoactive effects, binds primarily to CB1 receptors located in the brain and nervous system. This binding can alter the transmission of pain signals, effectively reducing the perception of pain. CBD, on the other hand, does not directly bind to these receptors but influences them in a way that enhances their pain-relieving properties. It also has anti-inflammatory effects that can further alleviate pain caused by nerve inflammation.
Methods of Administration
There are various ways to administer cannabinoids, each suited to different needs and preferences. Here are three common methods:
1. Inhalation (Vaping or Smoking):
Inhaling cannabinoids through vaping or smoking provides rapid relief, as the compounds enter the bloodstream quickly via the lungs. This method is often preferred by those seeking immediate pain relief, but it can irritate the respiratory system and is not recommended for individuals with lung conditions.
2. Oral (Edibles and Capsules):
Consuming cannabinoids in the form of edibles or capsules offers a longer-lasting effect, though the onset is slower compared to inhalation. This method is ideal for those needing extended relief throughout the day, but it requires careful dosing since the effects can be delayed and more potent.
3. Sublingual (Tinctures):
Tinctures are applied under the tongue, where the cannabinoids are absorbed directly into the bloodstream. This method strikes a balance between the quick onset of inhalation and the sustained effects of oral ingestion. It’s particularly useful for those who need consistent, moderate pain relief without the peaks and valleys associated with other methods.
Potential Side Effects
While cannabinoids can be effective in managing neuropathic pain, they are not without side effects. THC, for instance, can cause dizziness, sedation, and cognitive impairment, particularly at higher doses. CBD is generally well-tolerated, but some users may experience fatigue, changes in appetite, or mild gastrointestinal discomfort. Additionally, cannabinoids can interact with other medications, so it’s essential to consult with a healthcare provider before starting any new treatment.
Real-Life Example
Consider a person with diabetic neuropathy who experiences burning and tingling sensations in their feet, making walking painful. By using a CBD tincture twice daily, they may find that the discomfort is significantly reduced, allowing them to stay active without the constant burden of pain. Alternatively, someone with nerve pain from a spinal injury might use a THC vape pen for quick relief during flare-ups, while using CBD capsules daily to maintain overall pain management.
Conclusion
Cannabinoids like THC and CBD offer a new hope for those suffering from neuropathic pain, providing alternative relief when traditional treatments fall short. With various methods of administration available, individuals can tailor their use of cannabinoids to suit their specific needs. However, as with any treatment, it’s crucial to be aware of potential side effects and to consult with a healthcare professional to ensure safe and effective use. As research continues, cannabinoids may become a cornerstone in the management of nerve-related pain, improving quality of life for many.
Cannabis And Pain
Sports Injury Recovery and Marijuana: Can Cannabinoids Help?

In the realm of sports injury recovery, athletes and medical professionals are increasingly exploring alternative treatments to enhance healing and pain relief. One of the most promising areas of research involves cannabinoids—compounds found in marijuana—that are believed to offer potential benefits in reducing pain and inflammation. This article delves into the potential of cannabinoids in sports injury recovery, discusses methods of administration, and highlights the associated side effects.
Top Selling Item
GreenIVe Hemp Body Butter 17,500mg Per Oz Raw Natural Creamy Hemp Oil and Cocoa Butter Virgin Organically Grown. (8oz Jar)
Most Recommended
Hemp Cream Maximum Strength – Menthol Rub with Hemp Oil, Arnica, Lavender, Aloe Vera, Kava Kava, & Camphor – Natural Hemp Muscle Rub Cream for Skin, Muscles & Joints – ZenRenu, 4 oz
Understanding Cannabinoids and Their Role in Recovery
Cannabinoids, including cannabidiol (CBD) and tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), interact with the endocannabinoid system (ECS) in the human body. The ECS plays a crucial role in regulating pain, immune responses, and inflammation. CBD, known for its non-psychoactive properties, is particularly noted for its anti-inflammatory effects, making it a valuable tool for athletes recovering from injuries.

Methods of Administration
1. Topical Creams:
One of the most common methods of utilizing cannabinoids for injury recovery is through topical creams. These creams can be applied directly to the affected area, allowing cannabinoids to be absorbed through the skin. This localized application is beneficial for targeting specific areas of pain and inflammation, such as sprained ankles or sore muscles. For example, a professional basketball player might use a CBD-infused cream on their knee to alleviate pain from a minor ligament strain.
2. Vaping:
Another method of cannabinoid administration is vaping, where the compounds are inhaled into the lungs for rapid absorption into the bloodstream. Vaping allows for quick relief, making it a preferred method for those needing immediate pain reduction. However, it’s important to note that vaping can introduce harmful substances into the lungs and may not be suitable for everyone, especially those with pre-existing respiratory conditions.

Side Effects to Consider
While cannabinoids offer potential benefits, they also come with side effects that must be carefully considered:
– Impaired Coordination:
THC, the psychoactive component of marijuana, can impair motor skills and coordination. This effect can be particularly concerning for athletes who require precision and balance during their recovery period.
– Altered Judgment:
The use of cannabinoids, especially those containing THC, can affect decision-making abilities, leading to potentially risky behavior. For example, an athlete under the influence of THC might overestimate their recovery progress and attempt to return to play too soon, risking further injury.
– Respiratory Issues:
As mentioned, vaping can cause respiratory problems, which is a significant drawback for athletes who rely on optimal lung function.
Conclusion
Cannabinoids show promise in aiding recovery from sports injuries by reducing pain and inflammation. Topical creams and vaping are two popular methods of administration, each with its own advantages and drawbacks. However, it’s crucial to be aware of potential side effects, such as impaired coordination, altered judgment, and respiratory issues. Athletes considering cannabinoid use for recovery should consult with healthcare professionals to weigh the benefits against the risks.
Cannabis And Pain
Marijuana in HIV/AIDS Pain Management: A Comprehensive Overview

Introduction
HIV/AIDS patients often endure chronic pain as a significant part of their condition, impacting their quality of life. Managing this pain is crucial, and one alternative gaining attention is marijuana, also known as cannabis. This plant has been recognized for its anti-inflammatory and analgesic (pain-relieving) properties, which may offer relief to those suffering from HIV/AIDS-related pain.
How Marijuana Helps in Pain Management
Marijuana contains compounds called cannabinoids, with two primary ones being tetrahydrocannabinol (THC) and cannabidiol (CBD). These cannabinoids interact with the body’s endocannabinoid system, a complex cell-signaling system that plays a role in regulating pain, immune response, and inflammation. THC is known for its psychoactive effects, which can alter mood and perception, while CBD does not produce these effects but still contributes to pain relief.

Methods of Consumption
1. Smoking:
One of the most common methods of consuming marijuana is smoking. Inhalation allows for the rapid onset of effects, usually within minutes. This method is favored by many patients because it provides quick relief from pain. However, smoking can irritate the respiratory system, leading to coughing or bronchitis in some users.
2. Edibles:
Another popular method is consuming marijuana-infused edibles, such as gummies or baked goods. Edibles take longer to produce effects, typically between 30 minutes to 2 hours, but the relief they offer can last much longer than smoking. This method is beneficial for patients who prefer not to smoke or who need sustained pain relief over several hours. However, the delayed onset can sometimes lead to overconsumption, as patients may eat more than intended before the effects are felt.

Side Effects of Marijuana in HIV/AIDS Pain Management While marijuana can help manage pain, it is essential to be aware of potential side effects:
1. Appetite Changes:
Marijuana is known to increase appetite, commonly referred to as “the munchies.” This effect can be beneficial for HIV/AIDS patients who struggle with appetite loss, helping them maintain a healthy weight. On the other hand, some individuals may find this increase in appetite undesirable, leading to overeating.
2. Sedation:
Another common side effect is sedation or drowsiness, especially with higher doses of THC. This effect can be helpful for patients who have difficulty sleeping due to pain, but it may interfere with daily activities if it becomes too pronounced.
- Cognitive Impairment: THC can also affect cognitive function, leading to impaired memory, attention, and coordination. While these effects are generally temporary, they can be concerning for patients who need to stay alert and focused.
Real-Life Example
Consider John, an HIV-positive individual struggling with chronic pain and a poor appetite. By incorporating marijuana into his pain management plan, he finds that smoking a small amount in the evening relieves his pain and improves his appetite, allowing him to eat a full meal. He also sleeps better, though he notices some drowsiness the following morning. To balance this, he adjusts his dosage and timing to ensure he remains functional during the day.
Conclusion
Marijuana offers a promising alternative for managing pain in HIV/AIDS patients, with its anti-inflammatory and analgesic properties providing relief for many. Whether through smoking or edibles, patients can find a method that suits their needs while being mindful of potential side effects like appetite changes and sedation. As always, it is crucial to consult with a healthcare provider to determine the most appropriate and safe approach to using marijuana in pain management.
Cannabis And Pain
Peripheral Neuropathy Relief Through Cannabinoid Therapy: What You Need to Know
Peripheral neuropathy, a condition characterized by nerve damage leading to pain, tingling, and numbness in the extremities, can severely impact daily life. As traditional treatments often fall short, many are turning to cannabinoid therapy for relief. Cannabinoids like THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) and CBD (cannabidiol) are gaining attention for their potential in alleviating neuropathic pain. This article explores how these compounds may offer relief, focusing on topical application and oral ingestion, while also discussing potential side effects.

How THC and CBD May Help with Peripheral Neuropathy
THC and CBD interact with the endocannabinoid system (ECS), a complex network in the body that helps regulate pain, inflammation, and nerve function. In the context of peripheral neuropathy, these cannabinoids may reduce pain by modulating the ECS’s influence on nerve signals.
– THC: Known for its psychoactive effects, THC binds to CB1 receptors in the brain and nervous system, potentially reducing pain and inflammation associated with nerve damage.
– CBD: Unlike THC, CBD does not produce a “high.” Instead, it interacts with both CB1 and CB2 receptors, influencing the ECS indirectly. This can lead to reduced pain and inflammation without the psychoactive effects.
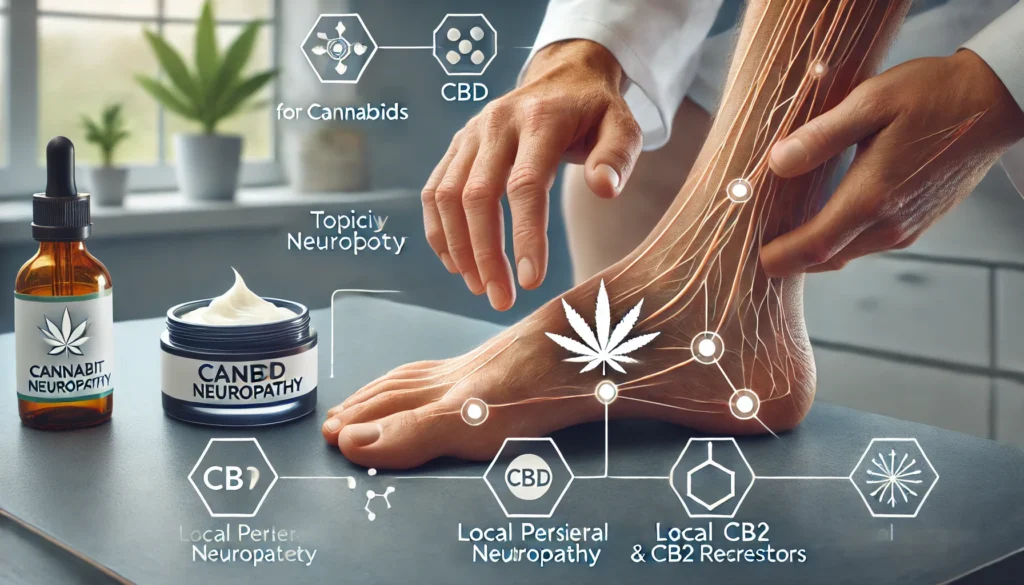
Methods of Cannabinoid Therapy for Peripheral Neuropathy
1. Topical Application:
– What It Is: This involves applying creams, balms, or oils infused with THC, CBD, or both directly to the affected area.
– How It Works: The cannabinoids are absorbed through the skin, interacting with local CB1 and CB2 receptors. This can provide localized relief without affecting the entire body.
– Real-Life Example: Imagine having a painful, tingling sensation in your hands. By rubbing a CBD-infused cream on your hands, you may experience reduced discomfort in that specific area.
2. Oral Ingestion:
– What It Is: Oral ingestion includes taking cannabinoids through capsules, edibles, or oils.
– How It Works: After ingestion, the cannabinoids are absorbed into the bloodstream and distributed throughout the body, offering more generalized relief.

– Real-Life Example: For those with widespread nerve pain, consuming a CBD oil tincture may help reduce overall discomfort, similar to taking a pain reliever that works throughout the body.
Side Effects of Cannabinoid Therapy While cannabinoid therapy offers potential benefits, it’s essential to be aware of possible side effects:
Dizziness:
Both THC and CBD can cause dizziness, especially when taken in higher doses. This occurs because cannabinoids can affect blood pressure and heart rate.
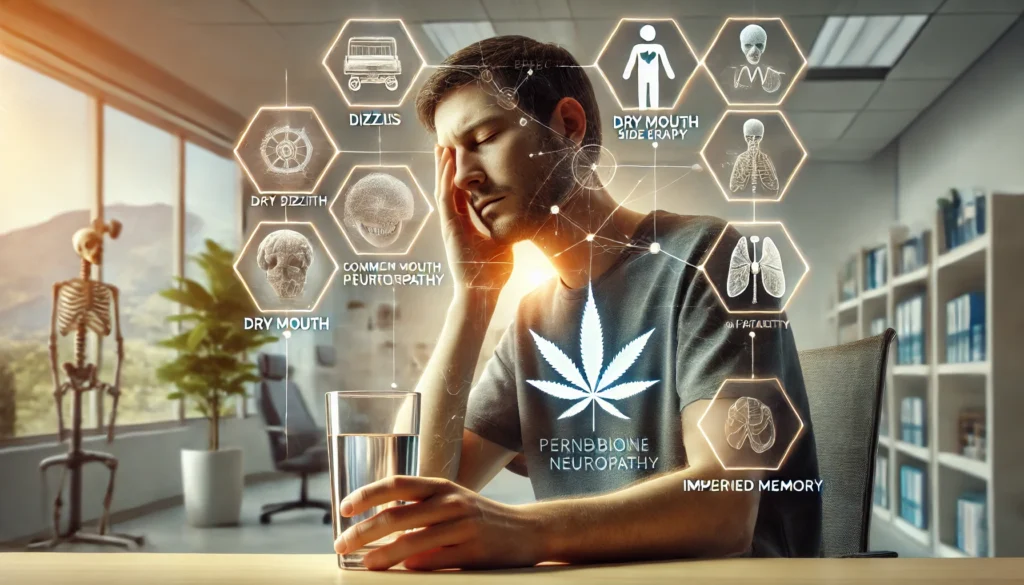

Impaired Memory:
THC, in particular, may lead to short-term memory impairment. This is due to its psychoactive effects on the brain’s hippocampus, the area responsible for memory formation.
Dry Mouth:
Cannabinoids can reduce saliva production, leading to a dry mouth sensation.
– Fatigue: Some users report feeling drowsy or tired after using cannabinoid products, which may be beneficial for nighttime use but problematic during the day.

Conclusion
Cannabinoid therapy, particularly through topical application and oral ingestion, shows promise in relieving peripheral neuropathy symptoms. However, it’s crucial to consider potential side effects and consult a healthcare provider before starting treatment. With proper use, cannabinoids may offer a valuable alternative or complement to traditional neuropathy treatments, improving quality of life for those affected by this challenging condition.
-

 Cannabis and Pet1 year ago
Cannabis and Pet1 year agoCBD vs. THC for Pets: What’s the Difference? – Understanding the Difference Between CBD (Cannabidiol) and THC (Tetrahydrocannabinol) for Pet Use Copy
-

 Canna solution1 year ago
Canna solution1 year agoHow Does Marijuana Affect REM Sleep?
-

 Canna solution1 year ago
Canna solution1 year agoWhat Are the Long-Term Effects of Using Marijuana as a Sleep Aid?
-

 Uncategorized1 year ago
Uncategorized1 year agoWhat Scientific Studies Support the Use of Marijuana for Sleep Improvement?
-

 Cannabis and Sustainibility1 year ago
Cannabis and Sustainibility1 year agoThe Role of Marijuana Leaves in Eco-Friendly Packaging Solutions
-

 Canna solution1 year ago
Canna solution1 year agoWhy Might Some People Experience Disturbances in Their Sleep After Using Marijuana?
-

 Canna solution1 year ago
Canna solution1 year agoHow Does Chronic Use of Marijuana Affect Sleep Over Time?
-

 Cannabis and Sustainibility1 year ago
Cannabis and Sustainibility1 year agoHarnessing the Potential of Marijuana Leaves in Teas and Beverages: Recipes and Benefits









